Functional high-throughput screening identifies the miR-15 microRNA family as cellular restriction factors for Salmonella infection | Nature Communications

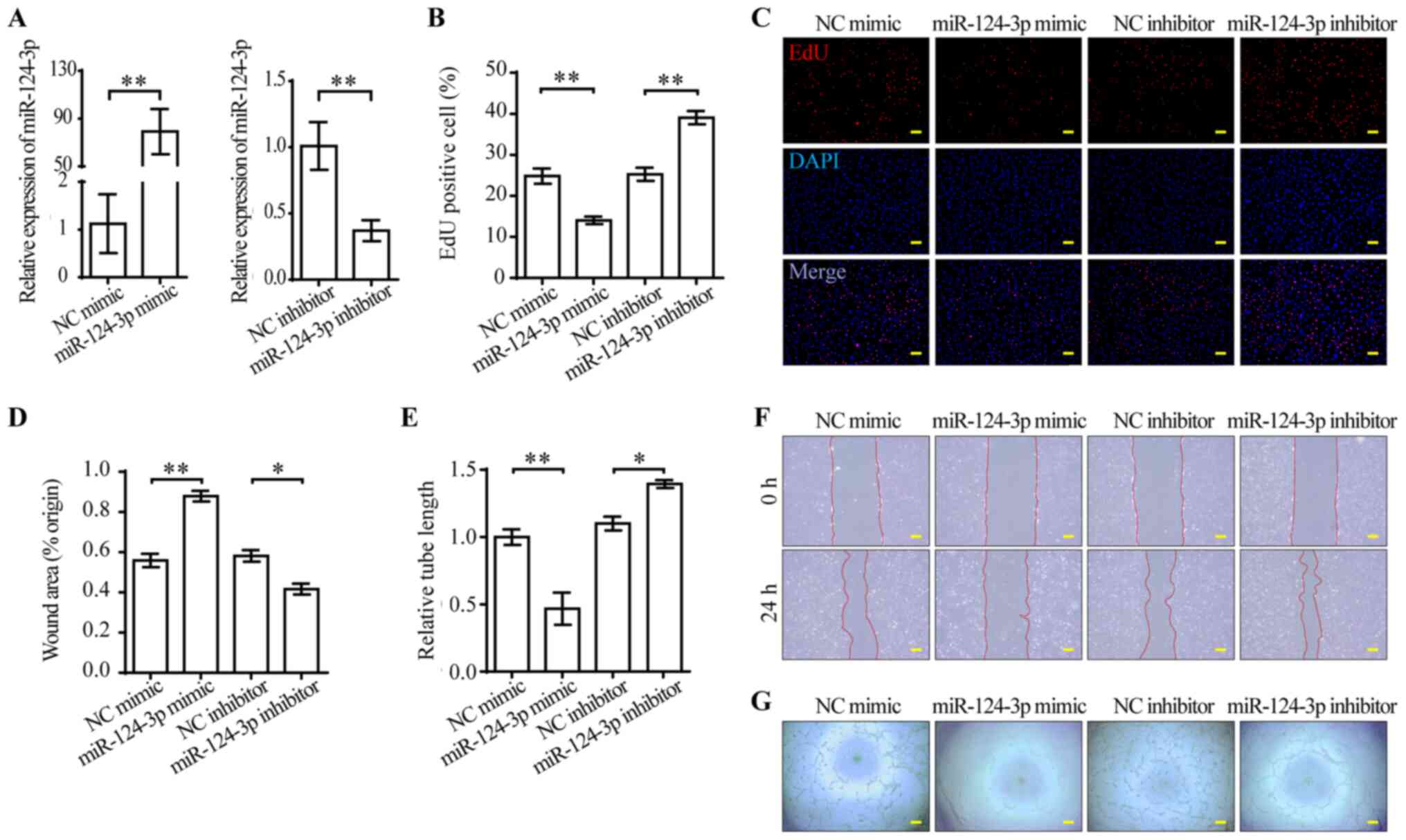
miR-34a directly targets tRNAiMet precursors and affects cellular proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis | PNAS

MiR‐339 inhibits proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell by targeting FGF signaling - Chen - 2017 - Physiological Reports - Wiley Online Library

miR-128-3p Is a Novel Regulator of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switch and Vascular Diseases | Circulation Research
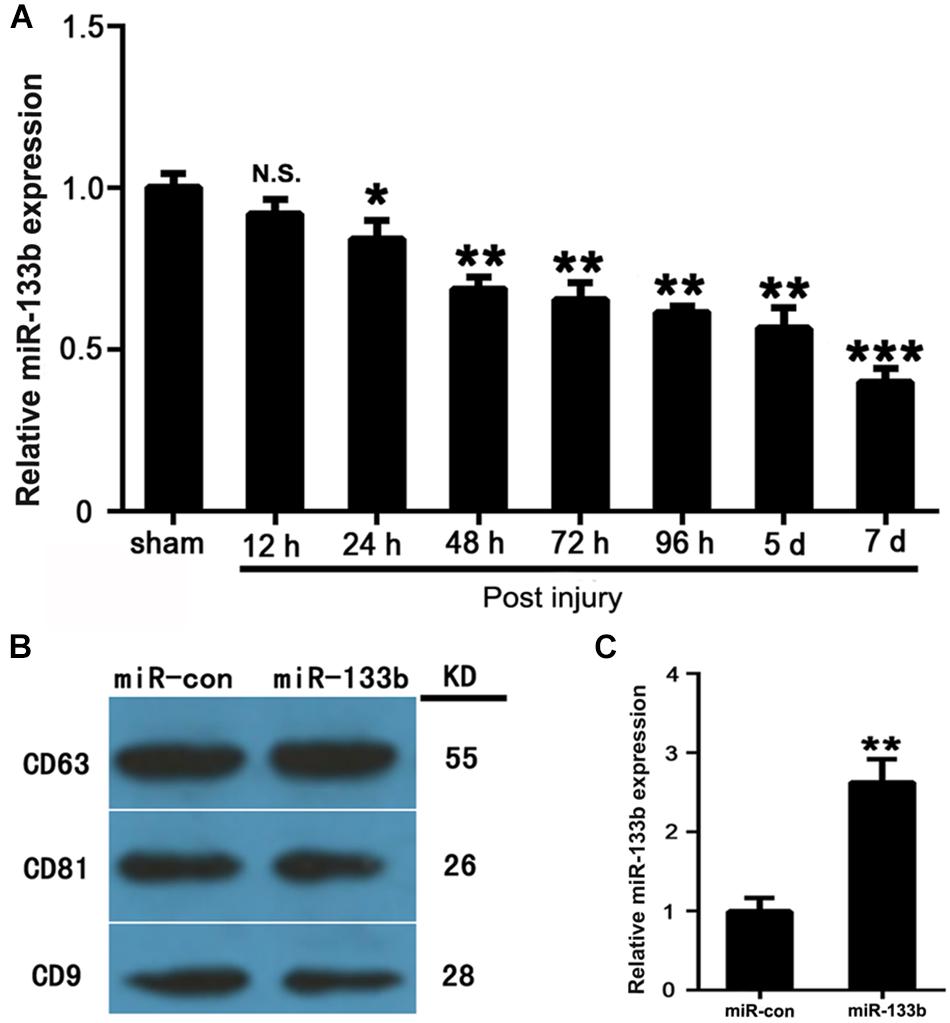
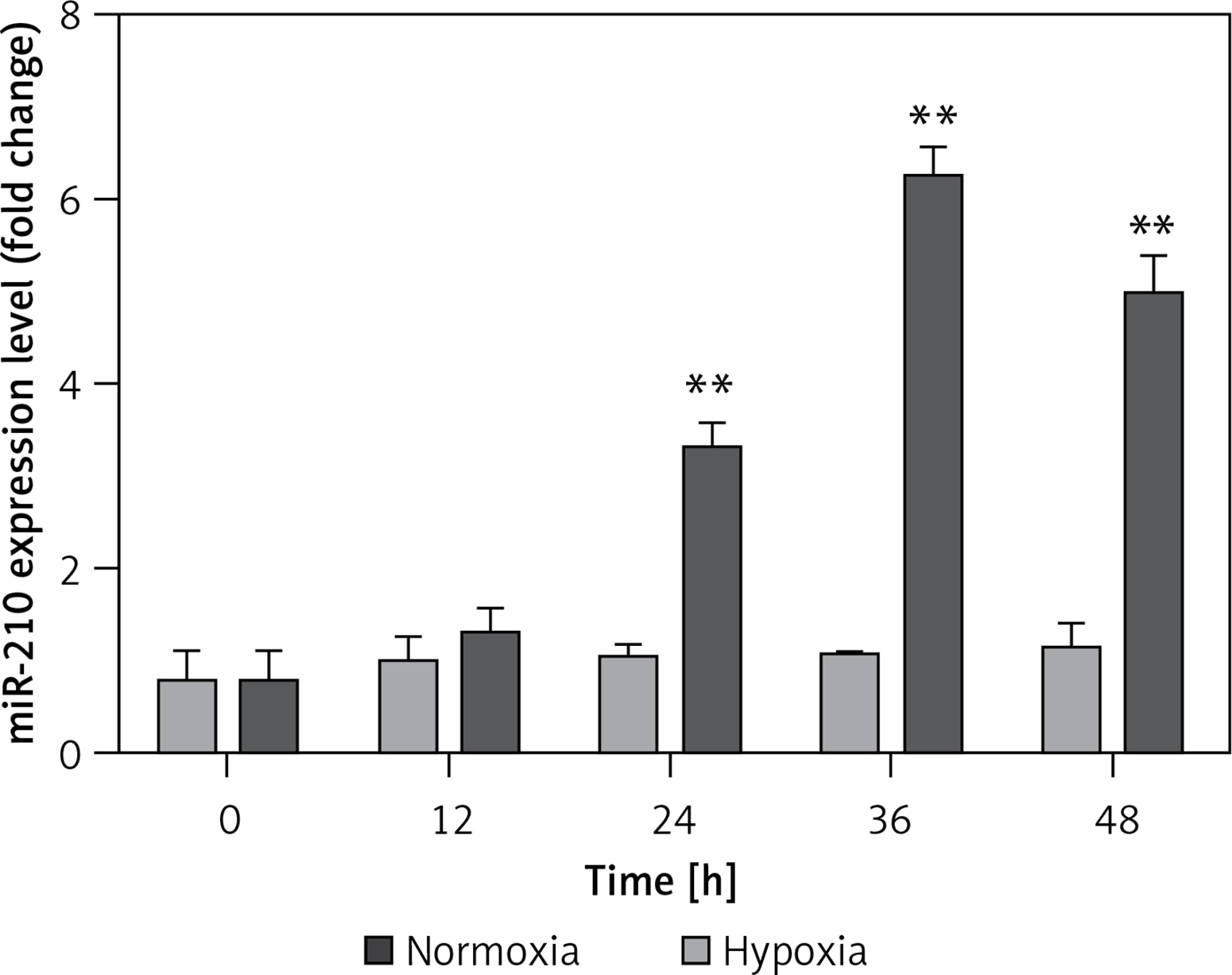
Frontiers | Exosomes Derived From miR-133b-Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Recovery After Spinal Cord Injury
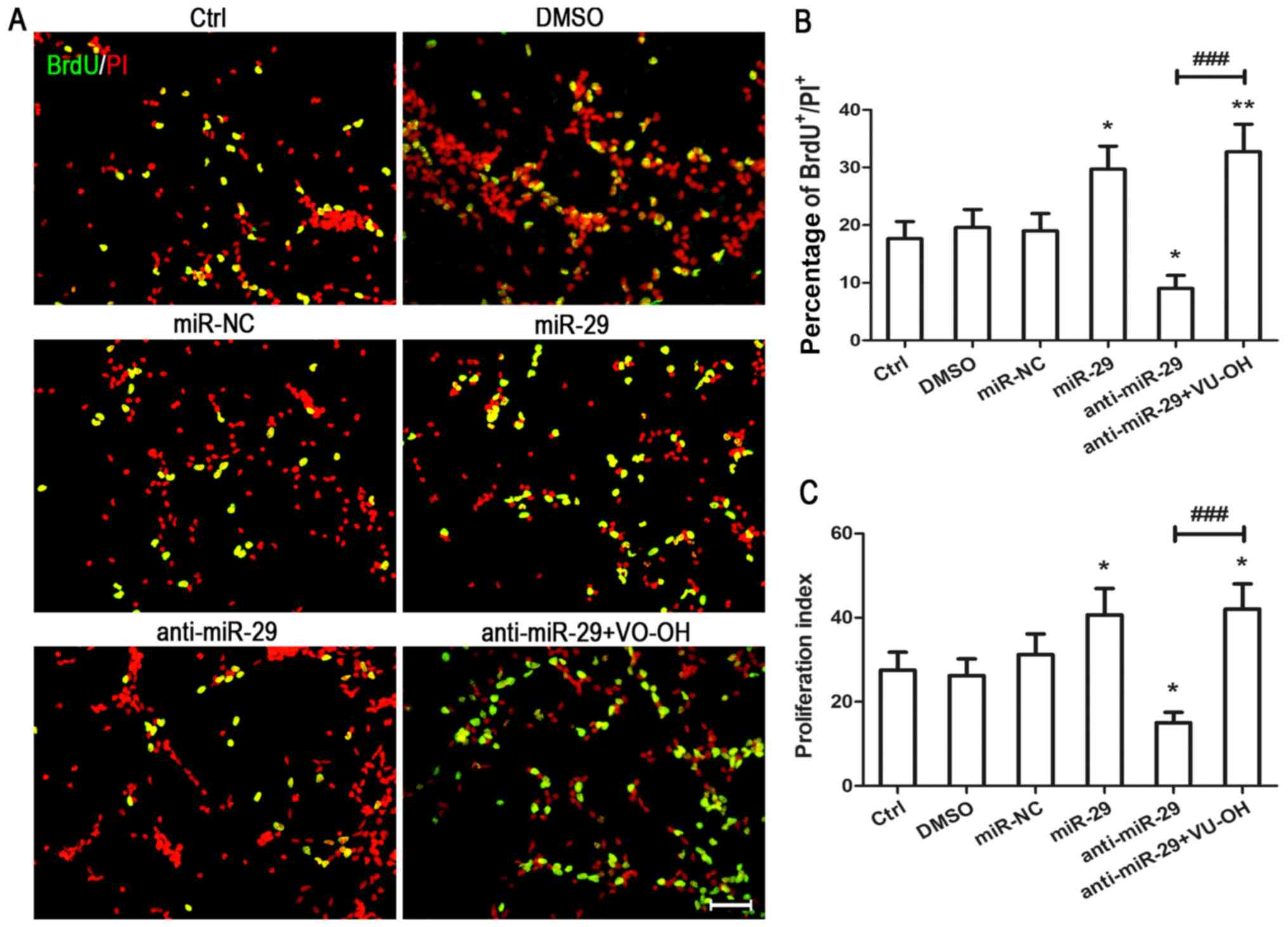
miR‑29 promotes the proliferation of cultured rat neural stem/progenitor cells via the PTEN/AKT signaling pathway

Hypermethylation of miR-205-5p by IR Governs Aggressiveness and Metastasis via Regulating Bcl-w and Src: Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids
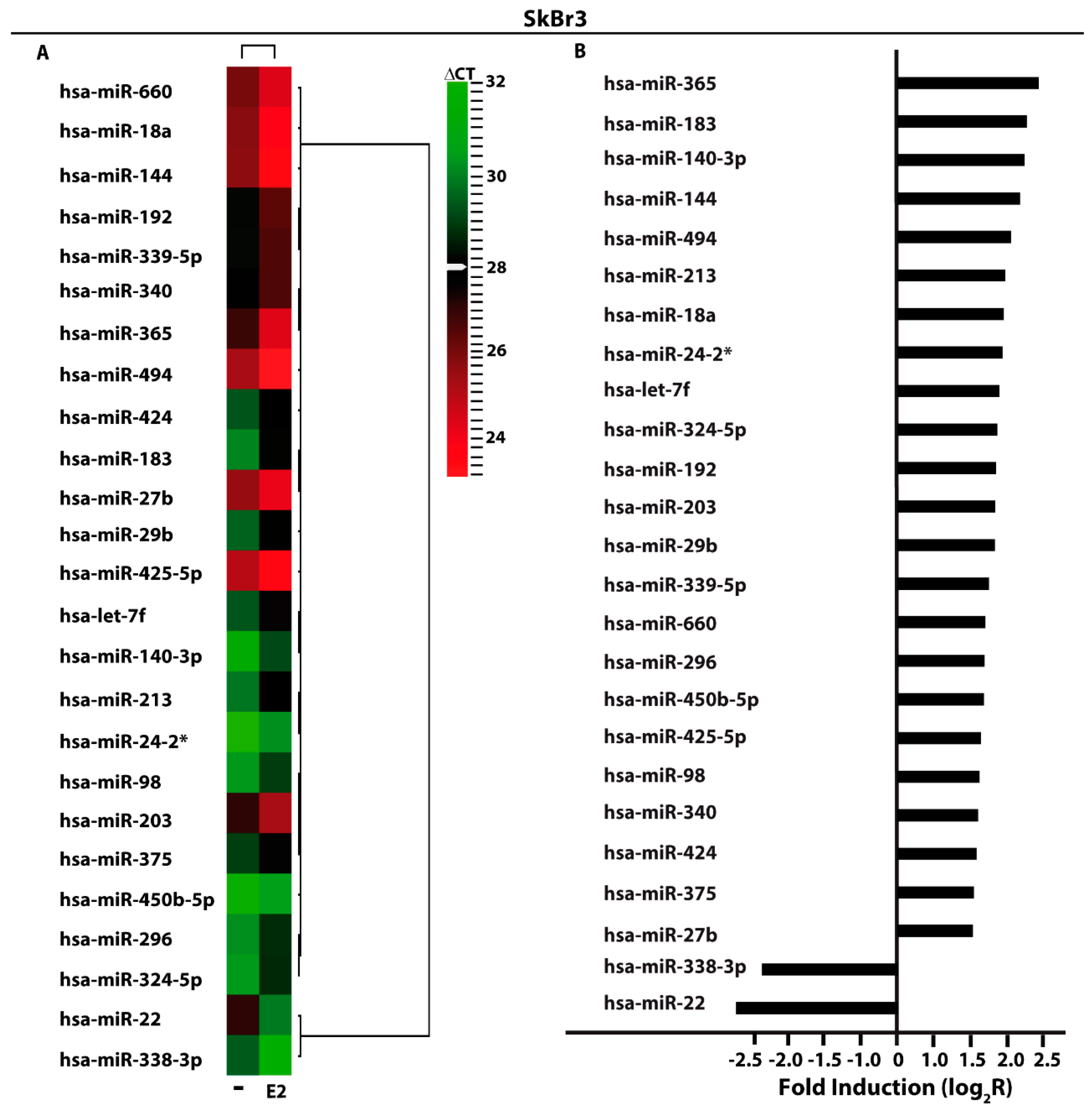
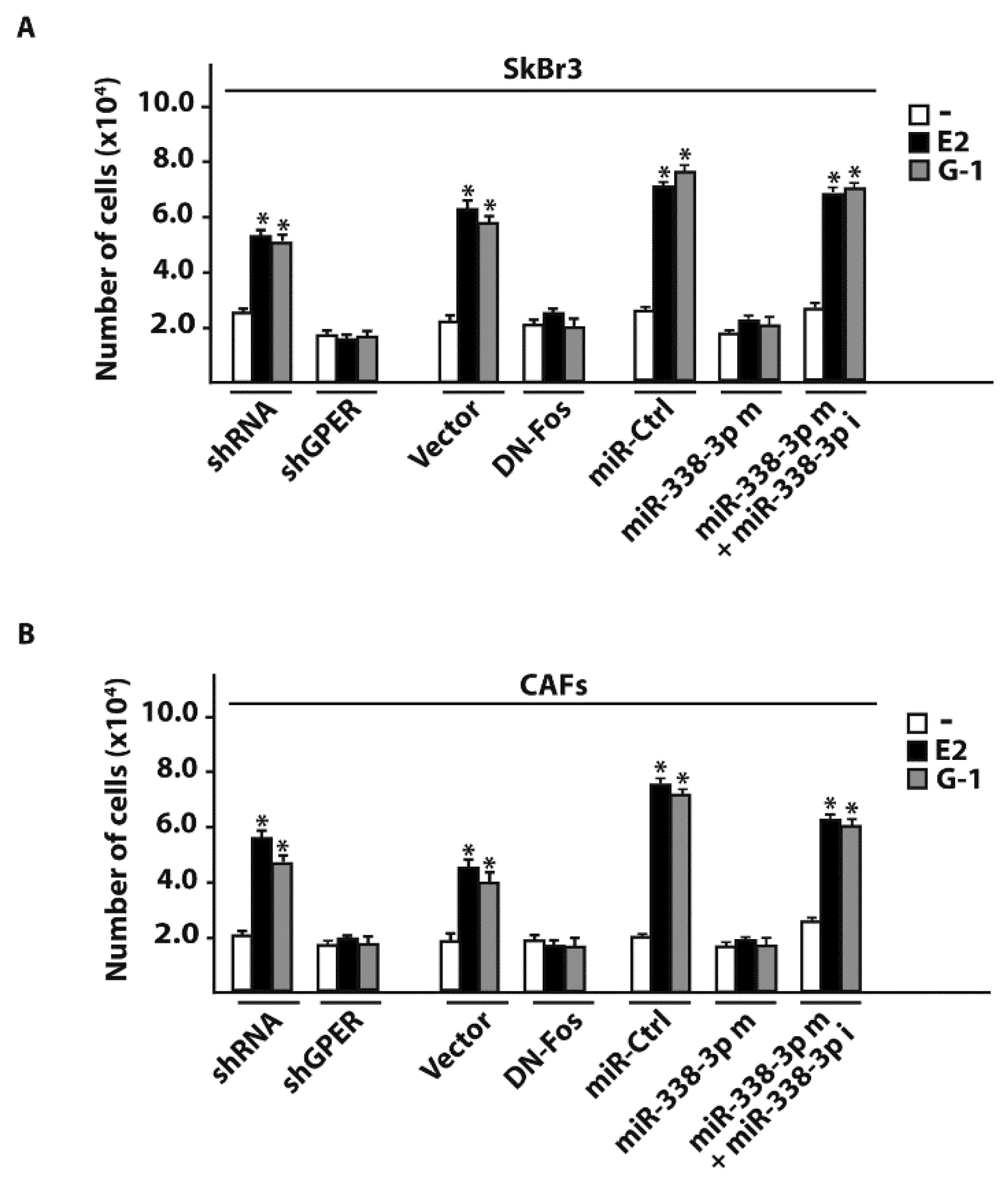
Cells | Free Full-Text | miR-338-3p Is Regulated by Estrogens through GPER in Breast Cancer Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) | HTML
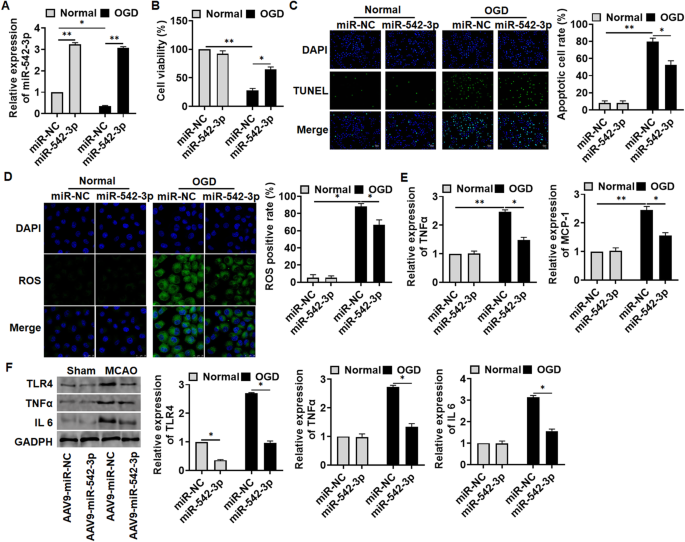
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome miR-542-3p suppresses inflammation and prevents cerebral infarction | Stem Cell Research & Therapy | Full Text

Amadori rearrangement products as potential biomarkers for inborn errors of amino-acid metabolism | Communications Biology
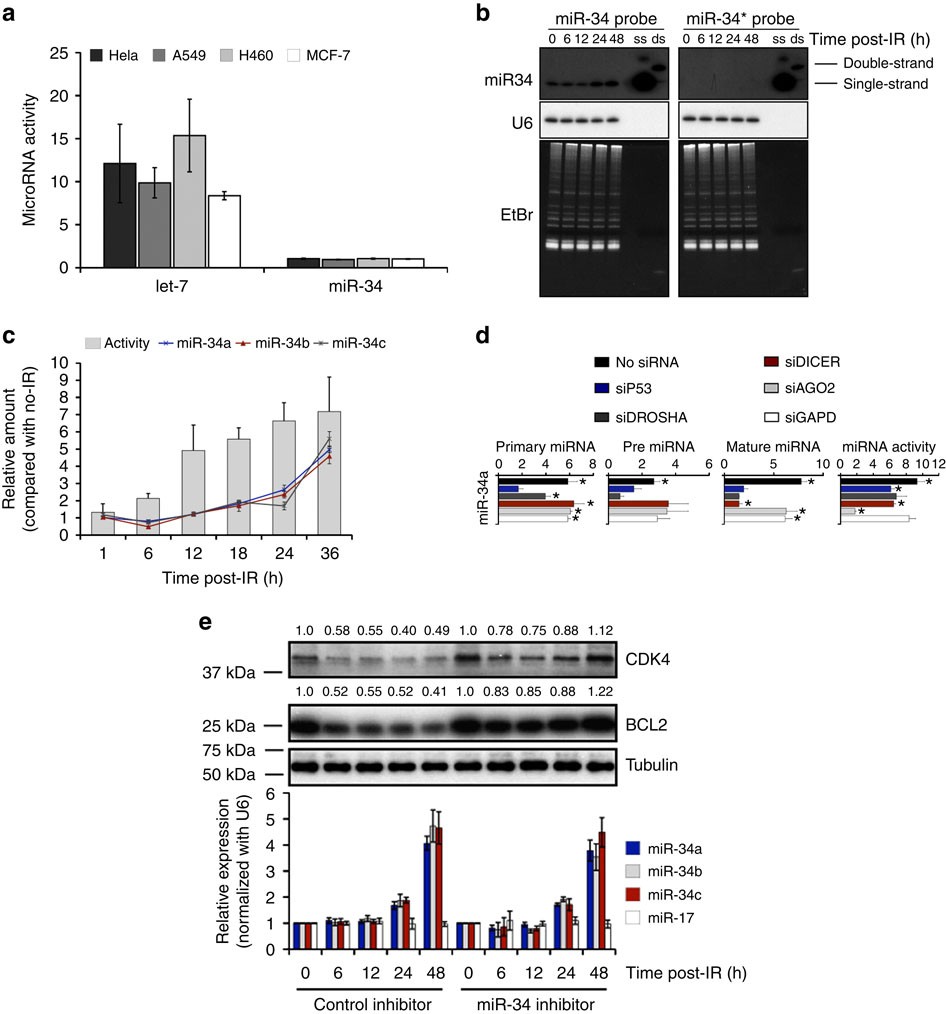
miR-34 activity is modulated through 5′-end phosphorylation in response to DNA damage | Nature Communications

miR‐181a/b downregulation exerts a protective action on mitochondrial disease models | EMBO Molecular Medicine
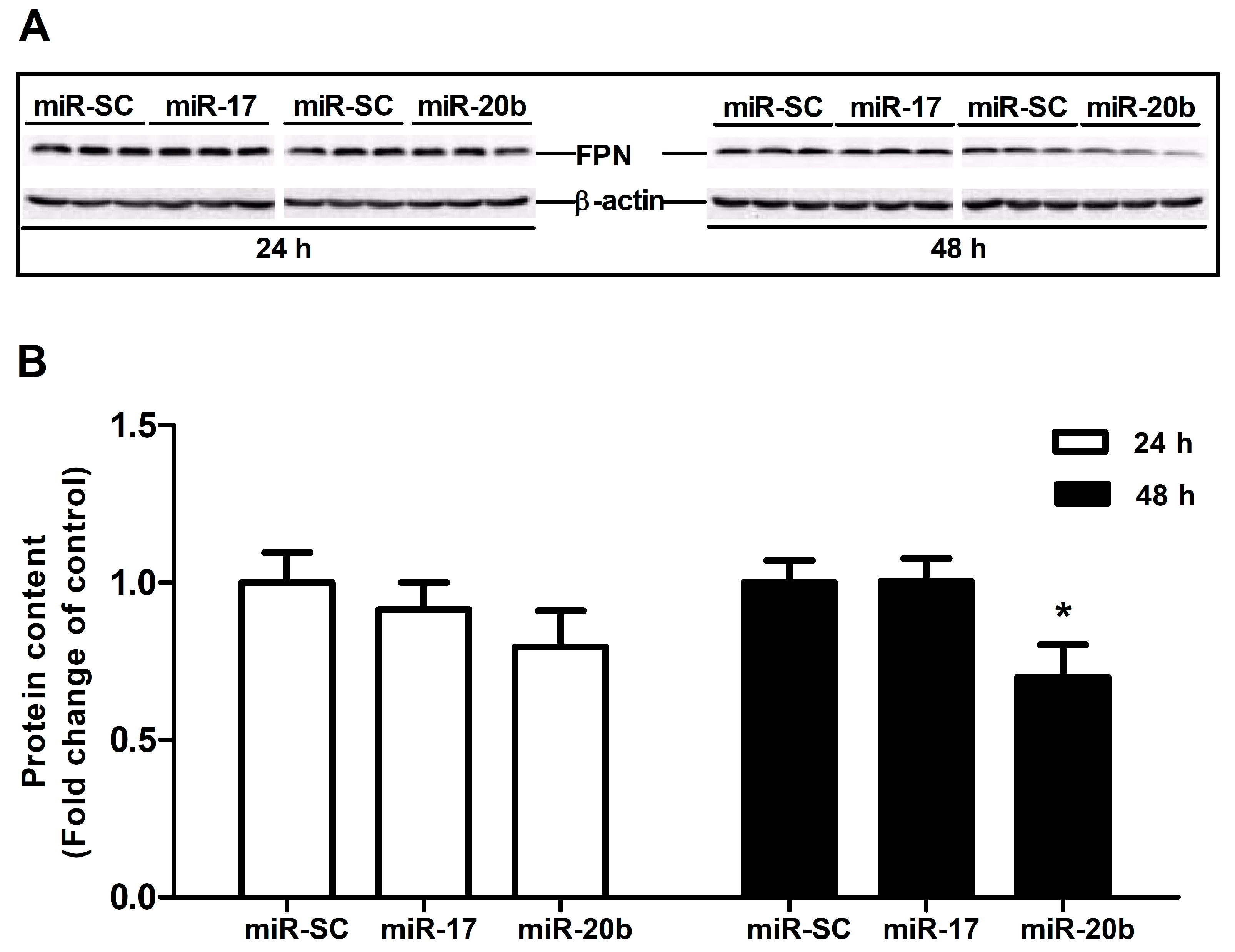
Cells | Free Full-Text | MiR-20b Down-Regulates Intestinal Ferroportin Expression In Vitro and In Vivo | HTML
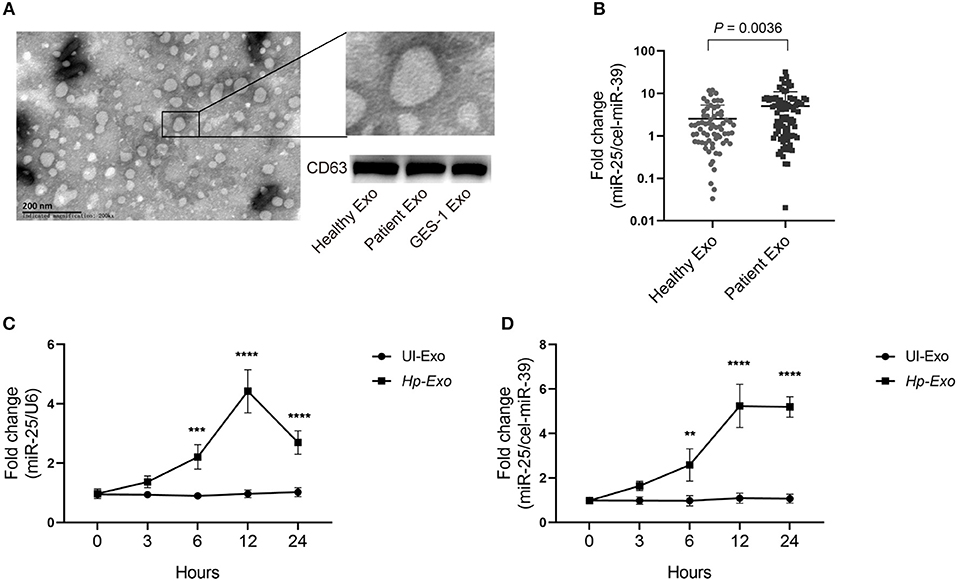
Frontiers | Exosome-Transmitted miR-25 Induced by H. pylori Promotes Vascular Endothelial Cell Injury by Targeting KLF2

Why is the Ir(III)-Mediated Amido Transfer Much Faster Than the Rh(III)-Mediated Reaction? A Combined Experimental and Computational Study | Journal of the American Chemical Society

Frontiers | MiR-204-3p Inhibited the Proliferation of Bladder Cancer Cells via Modulating Lactate Dehydrogenase-Mediated Glycolysis

miR-204-5p Represses Bone Metastasis via Inactivating NF-κB Signaling in Prostate Cancer: Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids
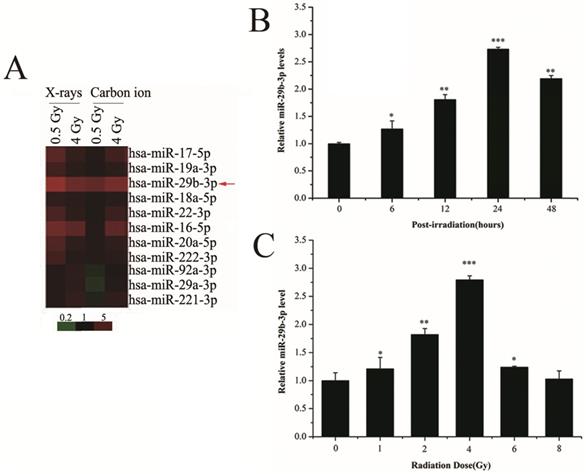
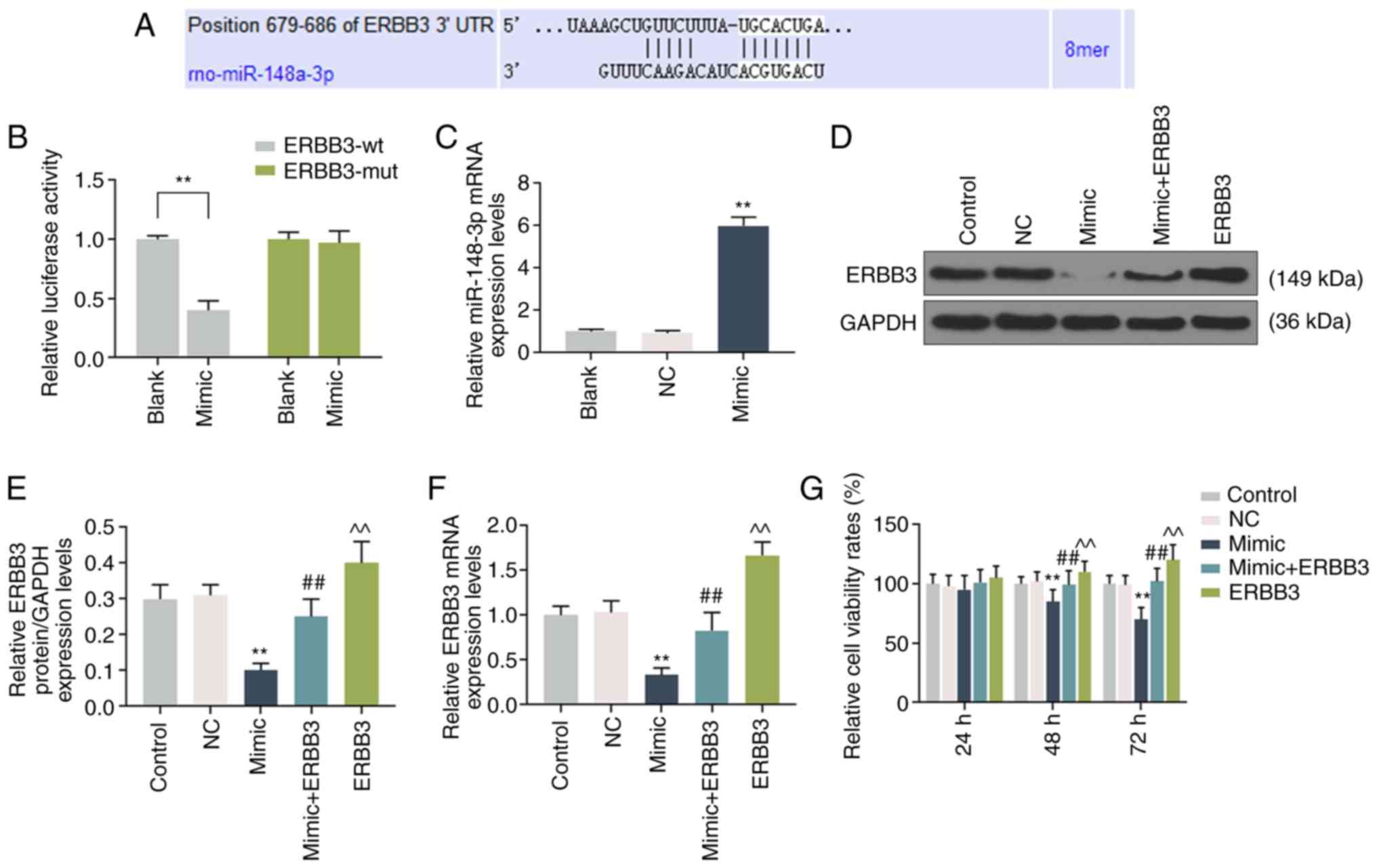
MicroRNA-29b-3p enhances radiosensitivity through modulating WISP1-mediated mitochondrial apoptosis in prostate cancer cells